While using Windows 10, you must have noticed that there are certain processes that needs to have Administrative rights to operate. For e.g. Command prompt. If you want to use Command prompt then you must have administration rights. If an application or process do not have such rights, then it may display several error messages Access Denied or No Permission. UAC also has the same function. User Account Control controls the apps opened by a user.
If an application developer has marked the application to require an administrator access token, then UAC performs action. This is done by using a development technique known as an embedded manifest.
Another situation is when UAC detected that the application is an installer or setup application. (Automatic detection can be disabled by using Group Policy.)
You can find out if a process is elevated or is permitted by UAC from Task Manager.
Steps to See if Process is Running as Administrator (elevated) in Windows 10
1. Press Alt+Ctrl+Del and select Task Manager.
2. Now click on the Details tab.
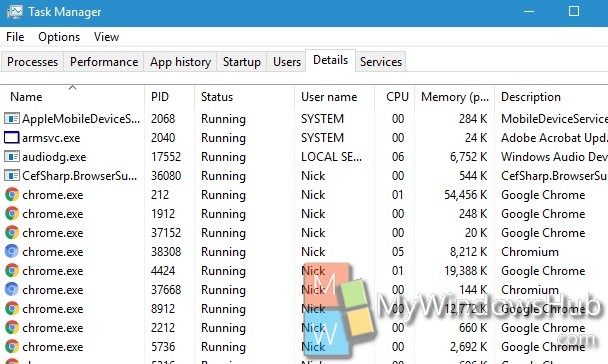
3. Now in the Options panel where options like Name, PID, Status etc are there, right click and tap on Select Columns.
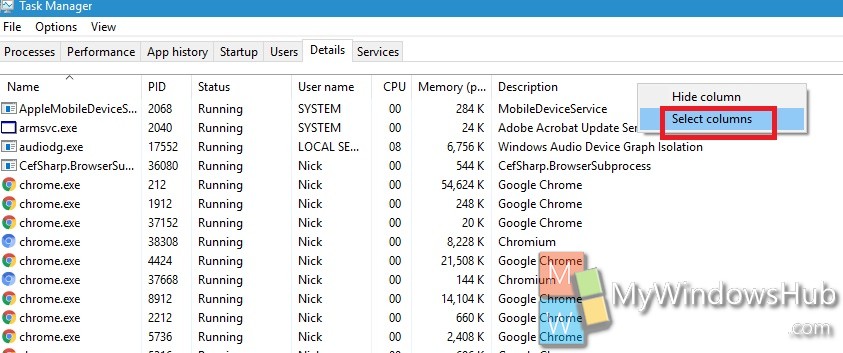
4. As the Select Columns appear, check the Elevated and UAC virtualization box.
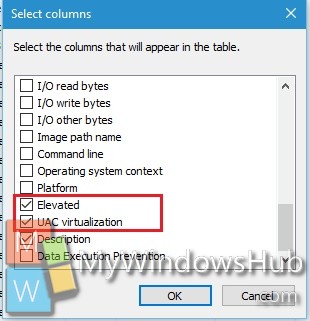
5. Now, the Elevated and UAC Virtualization columns will be added. You can check these options for different Apps.
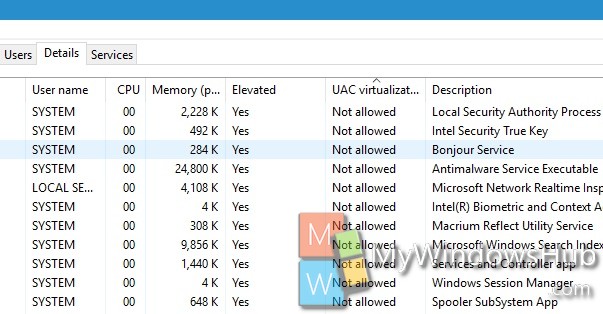
For Elevated, you can get either of the two results, Yes or No to explain whether the process is running as admin or not.
For UAC Virtualization, you can get any one of the following results,
Not allowed – Running as administrator (elevated).
Enabled – Subject to UAC virtualization.
Disabled – Not subject to UAC virtualization.

